Introduction
A recent investigation conducted by Cybernews has revealed the largest password leak in history. It has been confirmed that 16 billion login credentials, including passwords, have been exposed. This data concerns users of Apple, Facebook, Google, and other major online service providers, including social media platforms, VPNs, developer portals, and various government services.
And more:https://t.co/HPwV0ytWxn
— Kol Tregaskes (@koltregaskes) June 19, 2025
What happened
Researchers have concluded that this massive leak is the result of multiple “infostealers” (information-stealing malware). These malwares collected credentials directly from infected devices, rather than through a direct breach of the platforms themselves.
The stolen data has been compiled into 30 distinct exposed datasets. Each of these datasets is massive, containing from tens of millions to over 3.5 billion records. These records are composed of login credentials (usernames and passwords)are typically structured as URL followed by the corresponding login details.
The structured data enables access to all types of online services, including platforms such as Apple, Facebook, Google, GitHub, Telegram, and various government portals.
What is particularly concerning is that the majority of these datasets had never previously been reported as compromised, making them new, organized, and ready to use by malicious actors, according to researchers.
🚨 16 BILLION CREDENTIALS LEAKED — LARGEST DATA BREACH IN HISTORY!
— Numbers.lk (@numberslka) June 19, 2025
⭕ Cybernews researchers located 30 unsecured datasets holding ~16 billion login credentials from infostealer malware, each with tens of millions to 3.5 billion entries.
⭕ Affected services include Apple,… pic.twitter.com/7ARNdPa330
Our Recommendations
Password breaches are a serious and recurring issue that can lead to account hijacking and broader exposure of your digital identity. Given the scale of this incident, we strongly recommend you to take immediate action:
- Immediately change your passwords on all critical services.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA/2FA) wherever possible: This adds an additional layer of security.
- Use a password manager to generate and store strong, unique credentials for each service ensuring improved password hygiene.
- Adopt passkeys wherever available: Moving from passwords to passkeys is highly recommended. Google is recommending billions of users to adopt this more secure technology, while companies like Apple and Facebook have already announced their adoption.
Passkeys rely on what users already know such as facial recognition or fingerprint scans and are considered essential for protecting user identities.
The structured data enables access to all types of online services, including platforms such as Apple, Facebook, Google, GitHub, Telegram, and various government portals.
What is particularly concerning is that the majority of these datasets had never previously been reported as compromised, making them new, organized, and ready to use by malicious actors, according to researchers.
Cybersecurity Response Framework
- VMRay highlights that infostealer malware such as RedLine, Raccoon, and Vidar is a primary method of credential theft. These malicious programs collect sensitive data from browsers, VPNs, messaging apps, and crypto wallets to bypass security and enable further attacks including privilege escalation and ransomware. VMRay’s DeepResponse enables sandbox-based analysis of suspicious files or links, while TotalInsight helps validate threats using AI and correlation. Link
- CrowdStrike reports that attackers often use valid credentials to impersonate users and avoid detection. Common methods include phishing, brute-force attacks, LSASS memory dumping, and Kerberoasting. Falcon OverWatch recommends implementing strong MFA, maintaining good IT hygiene with Falcon Discover, and conducting continuous threat hunting to mitigate such threats. sensitive data from browsers, VPNs, messaging apps, and crypto wallets to bypass security and enable further attacks including privilege escalation and ransomware.
- According to Microsoft, Lumma Stealer (Storm-2477) is a Malware-as-a-Service that steals data from browsers, crypto wallets, and applications. It spreads via phishing, malvertising, and trojanized apps, and evades detection using process hollowing and protected C2 infrastructure. Microsoft advises reinforcing Defender for Endpoint and XDR, enabling phishing-resistant MFA, and using Microsoft Edge with Defender SmartScreen. Link
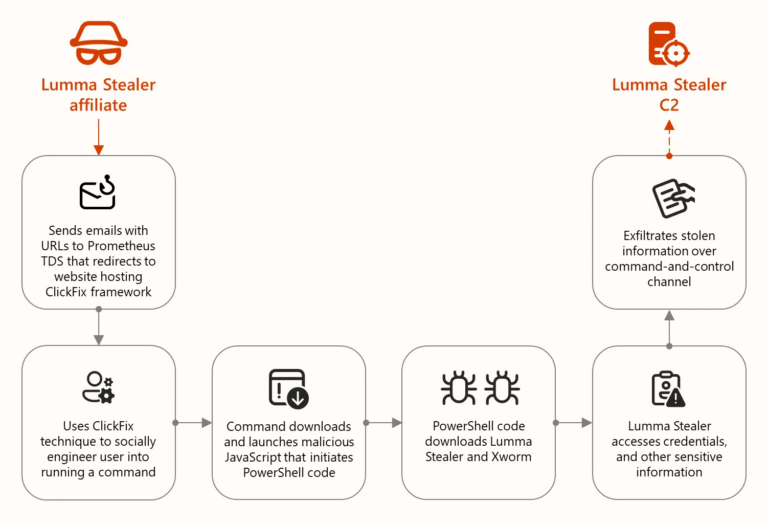
Our SOC (Security Operations Center) is heightening its vigilance, continuously monitoring for signs of attack or suspicious activity:
- Our Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) team is actively investigating to identify any potentially affected clients.
- Our Security Operations Center (SOC) is heightening its vigilance, continuously monitoring for signs of attack or suspicious activity.